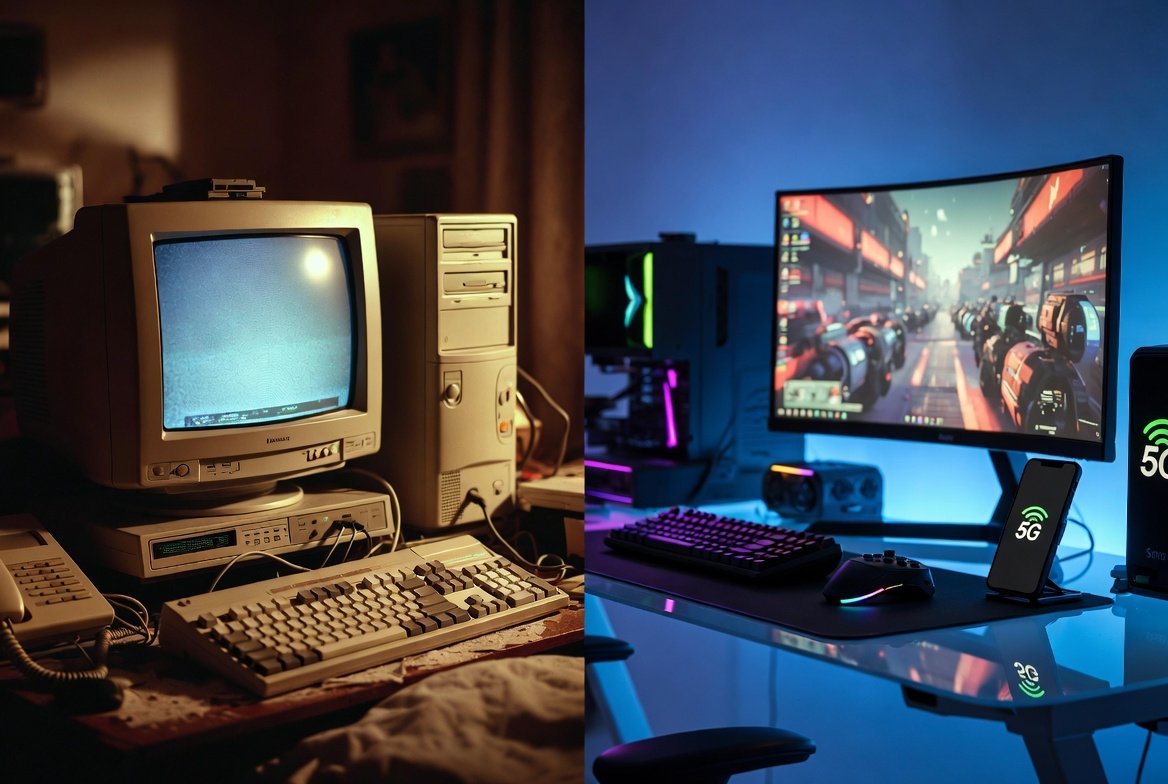
The internet developed through steady technical steps, each one changing online interaction. Early access relied on slow phone lines, while modern networks deliver near instant response. Gaming followed each phase closely, since multiplayer play depends on speed and stability. From text based games to competitive online arenas, network progress shaped how players connect, compete, and communicate across regions and time zones.
Dial Up and Early Online Access
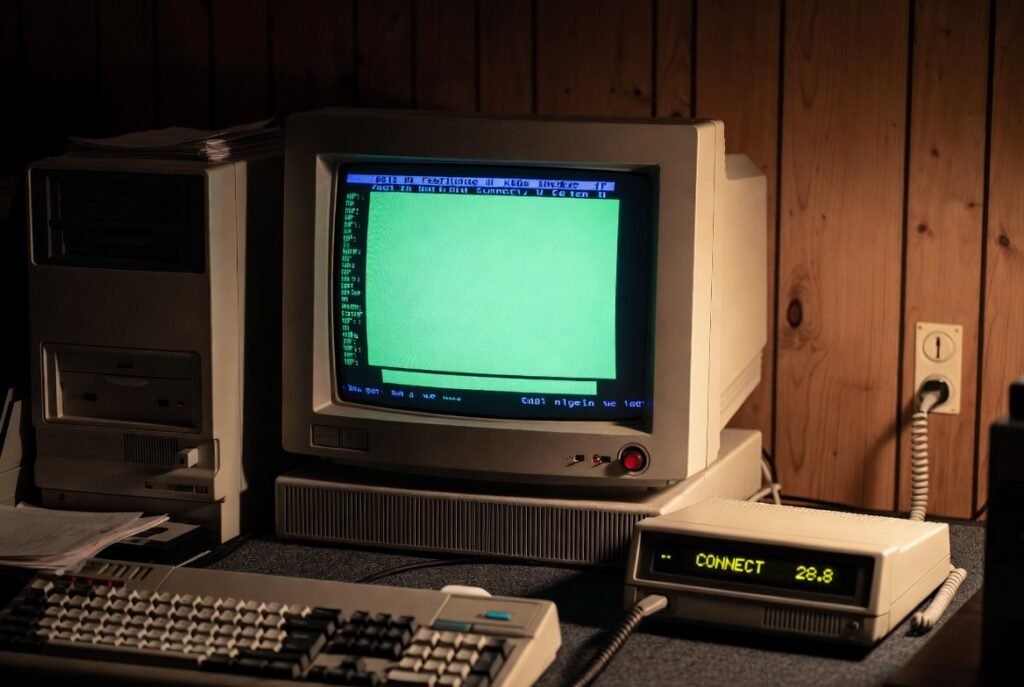

The 1990s Dial up access was based on telephone lines and 56 kbps modem access. The gaming that was played online in this case was concentrated on turn based games or text games or small games. Action-at-a-point was sluggish, and developers had to work around a small bandwidth and high frequency disconnections.
The Rise of Bulletin Boards and LAN Play
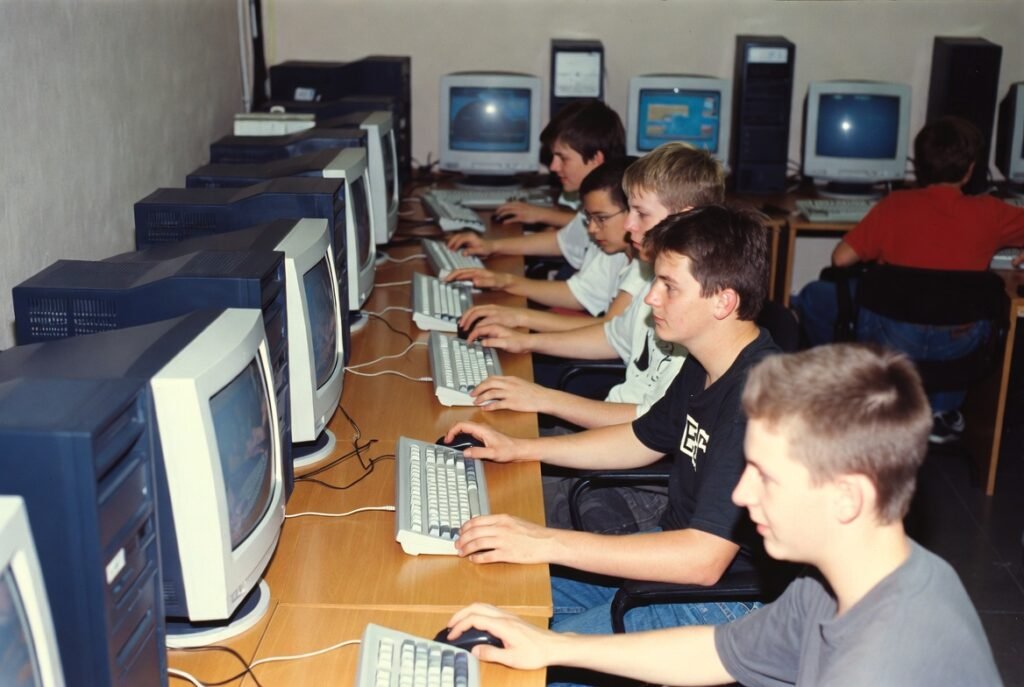

Before broadband adoption, bulletin board systems and local area networks supported early multiplayer gaming. Players shared files, strategies, and patches through direct connections. LAN parties gained popularity since local connections avoided network delay, offering faster response than home internet connections.
Broadband Changes Game Design
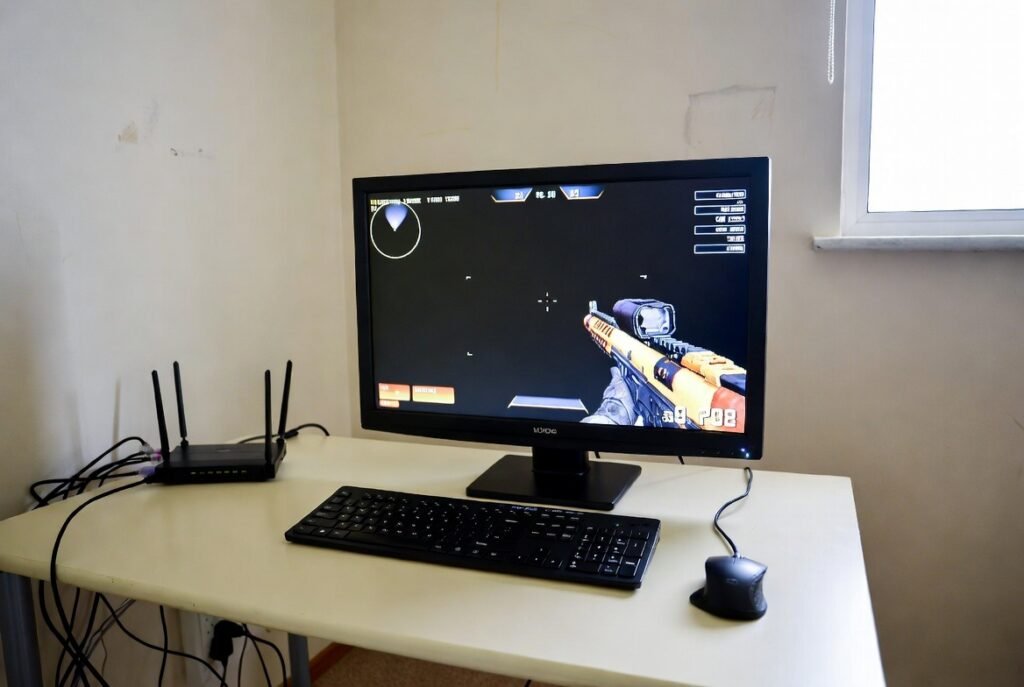

Stable connections with speeds more than 1 Mbps came with broadband services like DSL and cable in the early 2000s. Developers increased the number of multiplayer modes, voice chat, and increased the number of players. Online shooters and role playing games were popularized because real time communication has become feasible to home users.
Massively Multiplayer Online Games

Broadband growth supported large persistent online worlds. Games like early MMORPGs relied on constant server communication. Stable connections allowed shared economies, group missions, and long play sessions. Player communities expanded across countries, forming social structures linked through continuous network access.
Wi Fi and Mobile Internet Expansion

Wireless networking increased access beyond fixed desktops. Laptops and handheld devices supported casual online play. Mobile internet introduced simplified multiplayer formats. Gaming shifted toward shorter sessions, cloud saves, and account based progress accessible from multiple devices.
Latency Awareness in Competitive Gaming
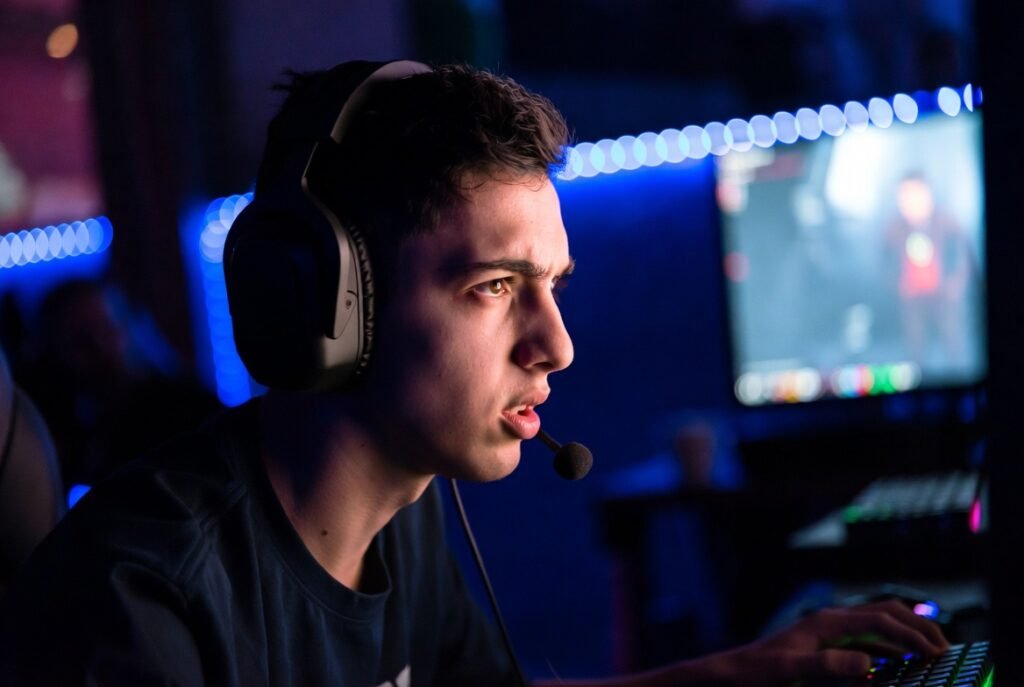

As online competition increased, players focused on latency and packet loss. Ping values became common metrics. Competitive gaming leagues required consistent connections. Developers optimized netcode to reduce delay effects, improving fairness in fast paced matches.
4G Networks and Always Connected Play

Fourth generation mobile networks delivered higher data rates and lower delay. Mobile esports and cross platform play expanded. Players joined matches during travel or breaks. Cloud based features such as live updates and online matchmaking gained wider use.
Streaming and Cloud Gaming Foundations
Improved networks supported live game streaming and early cloud gaming trials. Gameplay video reached audiences worldwide. Processing tasks shifted toward remote servers. Network stability became more important than local hardware for some gaming formats.
5G and Low Latency Gaming

Fifth generation networks focus on low delay and high capacity. Competitive mobile gaming benefits from faster response times. Augmented and virtual reality experiences rely on rapid data exchange. Developers explore real time multiplayer designs once limited to local systems.
Ongoing Network Evolution and Gaming Culture
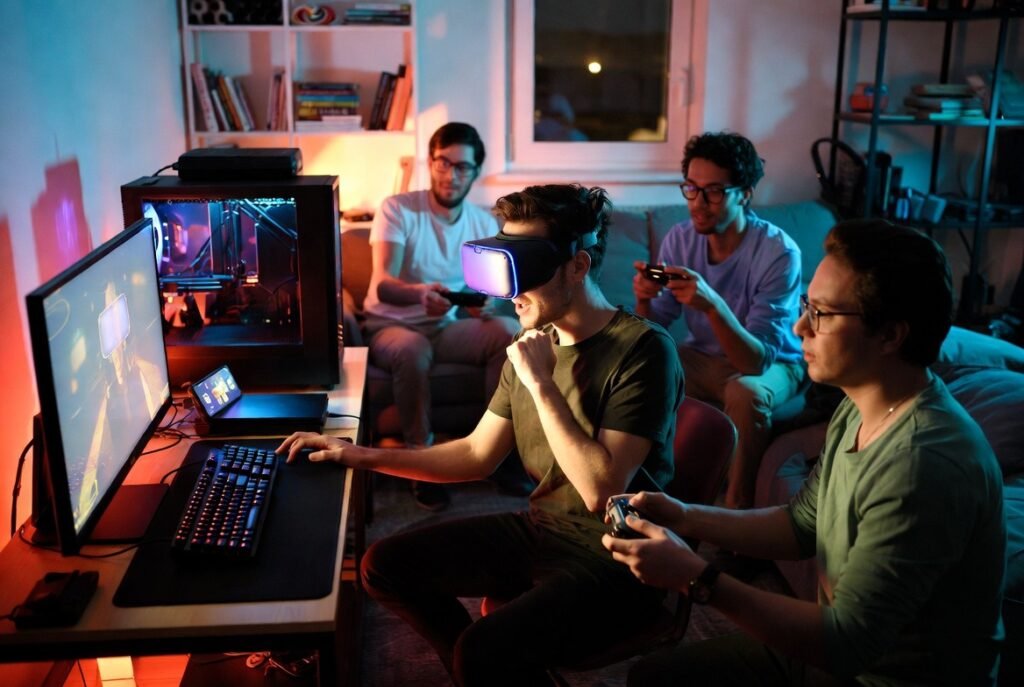

Internet history shows direct links between network capability and gaming habits. Faster access supports richer worlds, larger communities, and broader participation. As networks advance, gaming adapts through new formats, competitive structures, and social interaction models shaped by available speed and reliability.


